
Biohacking Anxiety
Anxiety affects over 40 million Americans annually, yet conventional approaches often miss the underlying neural circuitry. As a clinical neuroscientist who's analyzed 25,000+ brain scans, I've identified specific cortical signatures that reveal why traditional interventions fall short. The rise of biohacking offers precision-targeted strategies that address anxiety at the neural source—from dysregulated cingulate circuits to compromised vagal tone.
This article explores evidence-based biohacking techniques, from neurofeedback to hormetic stressors, designed to restore optimal brain function. We'll examine the four core regulatory systems that drive anxious states and how targeted interventions can retrain these circuits for lasting change.
Biohacking Anxiety: Neuroscientific Perspectives on Stress Management
Anxiety isn't just emotional distress—it's identifiable patterns of neural dysregulation across four core systems: arousal regulation (inability to downregulate activation), attention regulation (unstable focus control), sensory gating (hypersensitivity to stimuli), and emotional regulation (excessive intensity others can't access). Each category produces distinct QEEG signatures and responds to specific training protocols.
Cortical Regions & Neural Circuits in Anxiety
Key brain regions driving anxious states include:
Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC): Error detection and conflict monitoring. Overactivation creates persistent worry loops and catastrophic thinking patterns (Bush et al., 2000, Trends in Cognitive Sciences).
Posterior Cingulate Cortex (PCC): Self-referential processing and default mode network hub. Hyperactivity generates rumination and negative thought spirals (Whitfield-Gabrieli & Ford, 2012, Annual Review of Clinical Psychology).
Right Temporoparietal Junction (TPJ): Social threat detection and intention attribution. Dysfunction amplifies social anxiety and paranoid ideation (Samson et al., 2004, Brain).
Fast Alpha/Poor Alpha Blocking: Anxious individuals show elevated fast alpha (10-12 Hz) in frontal regions with impaired alpha suppression during cognitive tasks—a marker of hypervigilance and poor relaxation capacity.
QEEG Examples: Cortical Features of Anxiety
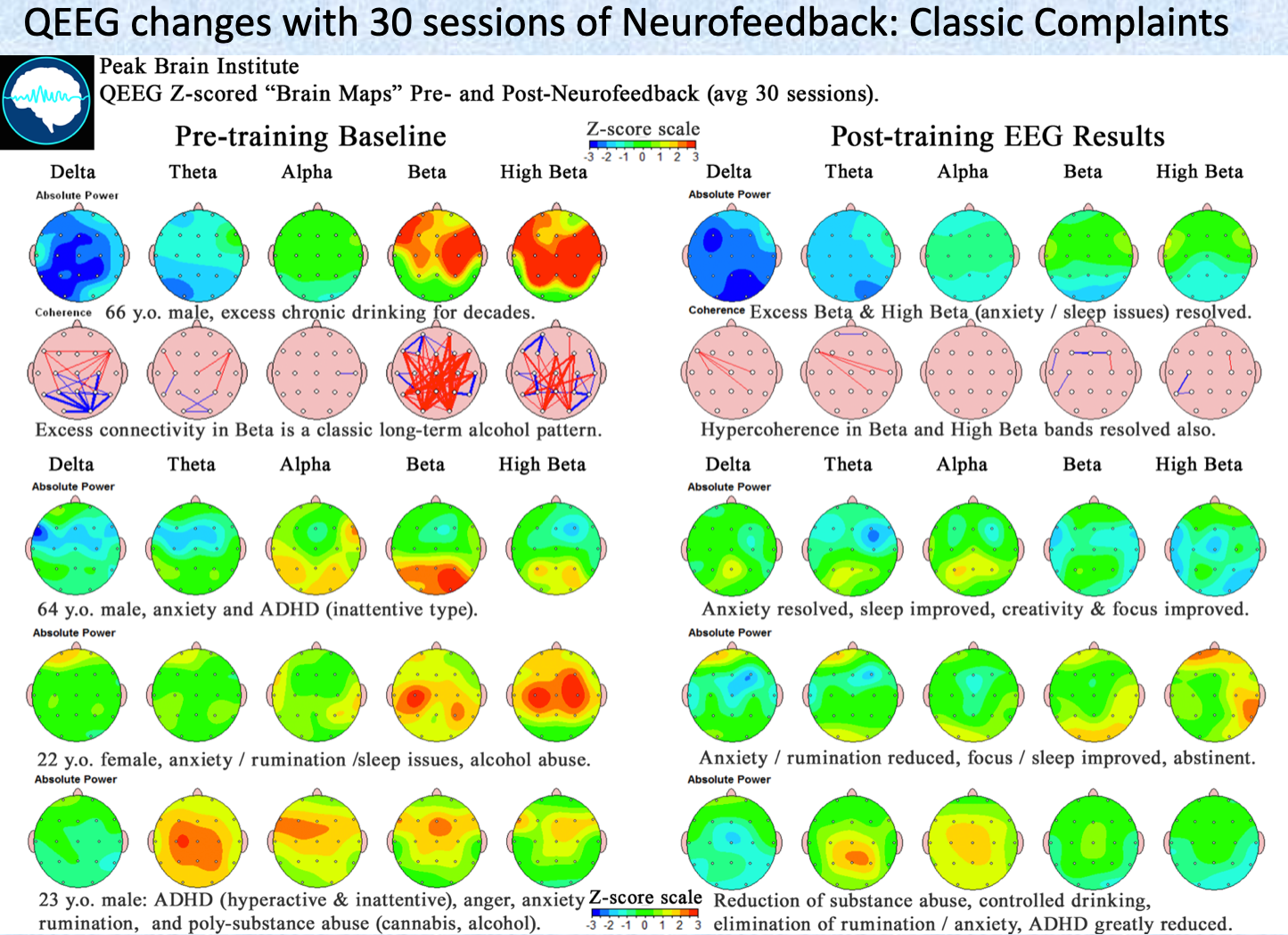
Biohacking Interventions
Understanding these dysregulated circuits allows precise targeting of interventions. Rather than generic "relaxation," we can train specific frequency patterns to restore optimal neural communication.
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Training
HRV measures beat-to-beat variation reflecting autonomic balance between sympathetic (fight-flight) and parasympathetic (rest-digest) systems. Higher HRV indicates stronger vagal tone—your nervous system's ability to recover from stress activation (Thayer & Lane, 2009, Journal of Affective Disorders).
Evidence-Based HRV Protocols:
Coherent Breathing: 5-6 breaths per minute with exhale 1.5x longer than inhale activates parasympathetic dominance within minutes. This specific ratio maximizes vagal tone enhancement (Gerritsen & Band, 2018, Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being).
HRV Biofeedback: Real-time feedback devices like emWave Pro train coherent heart rhythm patterns. Studies show 4-6 weeks of training increases HRV by 30-50% with corresponding anxiety reduction (McCraty & Shaffer, 2015, Frontiers in Psychology).
Zone 2 Walking: Light aerobic exercise at 180-age heart rate builds parasympathetic capacity long-term through improved cardiac vagal modulation.
Neurofeedback for Anxiety
Neurofeedback trains specific brainwave patterns through unconscious operant conditioning. The brain learns to maintain states that keep audio/visual feedback flowing smoothly, strengthening target neural pathways without conscious effort.
Precision Protocols:
SMR Training (12-15 Hz): Sensorimotor rhythm training at C3/C4 electrode sites strengthens thalamocortical circuits controlling arousal regulation. The same networks generating sleep spindles during rest also maintain calm focus when awake. Studies show 20+ sessions reduce anxiety scores by 40-60% (Hammond, 2005, Journal of Neurotherapy).
Alpha Protocol (8-11 Hz): Targets overactive cingulate circuits by promoting downregulation from excessive beta activity. Training sites typically include Pz (posterior cingulate) and Cz (midline cingulate) while inhibiting 13-20 Hz beta. Individual Alpha Frequency (IAF) assessment optimizes the target range for each person's unique neural signature.
Alpha-Theta Training: Deep state training combining alpha (8-12 Hz) and theta (4-8 Hz) at posterior sites (Pz, Oz). This protocol accesses trauma-processing states but requires stable baseline function—avoid with acute anxiety or active panic symptoms.
Walking and Movement
Physical movement directly modulates neurotransmitter systems driving anxiety. A 10-minute walk increases GABA activity in motor cortex for up to 2 hours post-exercise (Maddock et al., 2016, Journal of Neuroscience).
Targeted Movement Protocols:
Forest Bathing (Shinrin-yoku): 20 minutes in natural environments reduces cortisol by 15-20% compared to urban walking while increasing NK immune cell activity (Park et al., 2010, Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine).
Walking Meditation: Combines rhythmic movement with present-moment attention, training both attention regulation and arousal control simultaneously.
Breathing Techniques
Controlled breathing directly influences autonomic balance through vagal nerve stimulation. Specific patterns produce measurable changes in neural activity within 30 seconds.
Clinically Validated Techniques:
Box Breathing: 4-4-4-4 count (inhale-hold-exhale-hold) activates prefrontal cortex while calming amygdala reactivity. Navy SEAL research shows improved performance under stress (Norris, 2020, Military Medicine).
4-7-8 Breathing: Parasympathetic dominance through extended exhale phase. The 2:1 exhale-to-inhale ratio maximizes vagal stimulation for rapid anxiety reduction.
Nootropics for Anxiety
Targeted supplementation can support neural circuits underlying anxiety regulation, though individual response varies significantly.
Research-Backed Options:
L-Theanine (200mg): Increases alpha waves in anterior cingulate while boosting GABA activity without sedation. Effective within 30-45 minutes (Nobre et al., 2008, Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition).
Ashwagandha (300-500mg): Adaptogen reducing cortisol by 25-30% in stressed individuals while improving stress resilience over 8+ weeks (Chandrasekhar et al., 2012, Indian Journal of Medical Research).
Magnesium Glycinate (200-400mg): NMDA receptor modulation and GABA potentiation. Deficiency affects 50%+ of adults and directly correlates with anxiety severity (Boyle et al., 2017, Nutrients).
Hormetic Approaches: Sauna and Cold Exposure
Hormesis—beneficial adaptation to mild stress—builds nervous system resilience through controlled challenge exposure. These interventions create "antifragility" by training appropriate stress responses.
Evidence-Based Hormetic Protocols:
Sauna Therapy: 15-20 minutes at 80-100°C increases heat shock proteins, endorphins, and BDNF while reducing anxiety markers. Finnish studies show 4+ sessions weekly reduce anxiety disorders by 30% (Laukkanen et al., 2018, Psychosomatic Medicine).
Cold Exposure: 2-3 minute cold water immersion (50-59°F) or cold showers activate vagal nerve while building stress tolerance. The adaptation phase trains your system to recover quickly from sympathetic activation (Shevchuk, 2008, Medical Hypotheses).
Additional Evidence-Based Interventions
Mindfulness Training: 8-week MBSR programs reduce anxiety by training attention regulation and emotional reactivity. fMRI studies show decreased amygdala reactivity with increased prefrontal control (Goyal et al., 2014, JAMA Psychiatry).
Sleep Optimization: Anxiety and sleep disruption create bidirectional dysfunction. Blue light blocking 2 hours before bed, consistent sleep timing, and cool temperatures (65-68°F) restore circadian rhythm regulation essential for emotional stability.
Gut-Brain Axis: Probiotic strains like Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 reduce anxiety through vagal nerve communication. The gut produces 90% of serotonin, making microbiome health crucial for mood regulation (Messaoudi et al., 2011, British Journal of Nutrition).
Conclusion
Biohacking anxiety requires understanding the specific neural circuits driving your symptoms. Rather than generic relaxation, target the four core regulatory systems through precision interventions: HRV training for autonomic balance, neurofeedback for cortical regulation, movement for neurotransmitter optimization, and hormetic stress for resilience building.
The key is matching intervention to circuit dysfunction. Overactive cingulate circuits respond to alpha training, while poor vagal tone requires HRV biofeedback. QEEG assessment reveals your unique pattern, allowing personalized protocol selection.
As neuroscience advances, our ability to tailor these interventions grows more precise. The future lies not in one-size-fits-all approaches, but in understanding your brain's specific signature and training it accordingly.
Related Articles
Biohacking Brain Fog: Restoring Mental Clarity
Your thoughts feel slow. Words don't come easily. You're staring at your computer screen, but nothing's happening—just mental static where clarity should be.
Biohacking with EEG Phenotypes: Predict Your Brain Function
Your QEEG isn't just a brain map. It's a phenotype—a stable electrical signature that predicts how you process information, regulate attention, and respond to interventions.
Biohacking Learning: Evidence-Based Skill Acquisition
Your brain's "factory settings" aren't optimized for learning. Discover evidence-based protocols for accelerated skill acquisition through neuroplasticity and strategic training.
About Dr. Andrew Hill
Dr. Andrew Hill is a neuroscientist and pioneer in the field of brain optimization. With decades of experience in neurofeedback and cognitive enhancement, he bridges cutting-edge research with practical applications for peak performance.
Get Brain Coaching from Dr. Hill →